- Неплохой базовый мануал (часть инфы ниже оттуда) что такое DoS от CISA / FBI и крупных компаних в IT (Akamai, Cloudflare, Google) с меткой TLP:clear на безграничное распространение: Understanding and Responding to Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks_508c
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) are releasing this joint distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack guidance
- Очень хороший мануал от Juniper с описанием атак и методов защиты от них в JunOS
- БИФИТ Mitigator – Российское решение на базе стандартных серверов
- Статья по тюнингу параметров ядра Linux для большей устойчивости в DoS/DDoS сценариях (настройки серверные)
DOS/DDOS теория
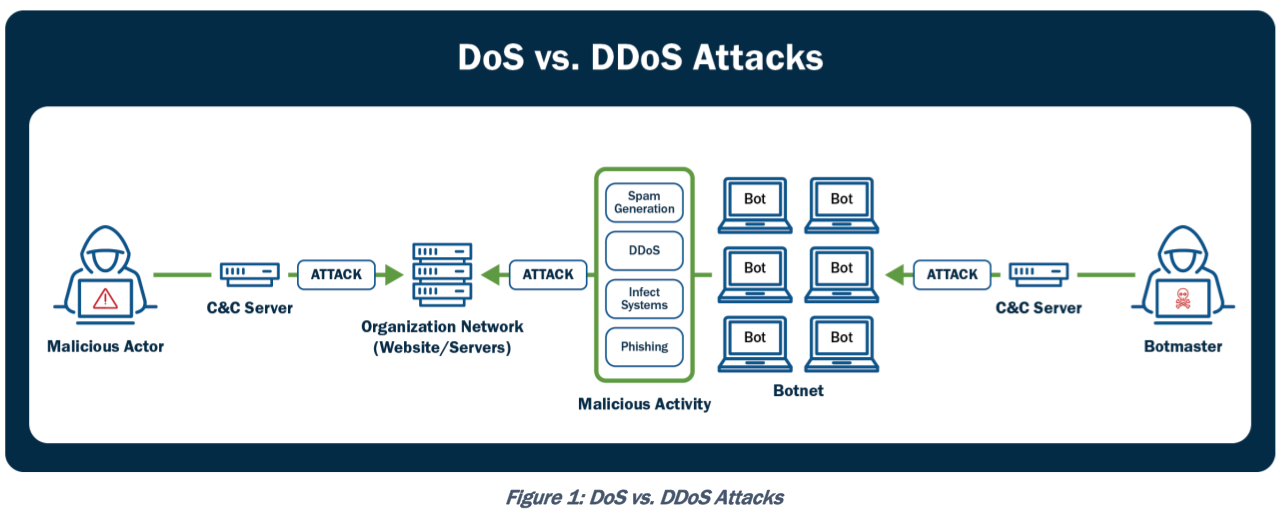
DOS/DDOS (dns lookup, half-open attacks like syn flood; ddos = dos + botnet => flood guard) – отправляем большое количество каких-либо пакетов/запросов/ответов для отказа в обслуживании сервиса из-за нехватки ресурсов (процессинговых, памяти, сетевых и проч). DDOS – Distributed DoS (напр. используя botnet).
Это если в среднем. По факту даже атаку с одним или несколькими пакетами зачастую называют DoS – если в результате этой атаки произошел тот самый Denial of Service. Примером такой атаки можно считать TCP SACK PANIC, когда небольшое количество скрафченных TCP пакетов с минимальным MSS и использованием SACK приводит к отказу системы из-за уязвимости в коде ядра Linux.
A remote user can trigger this issue by setting the Maximum Segment Size(MSS) of a TCP connection to its lowest limit of 48 bytes and sending a sequence of specially crafted SACK packets. Lowest MSS leaves merely 8 bytes of data per segment, thus increasing the number of TCP segments required to send all data.
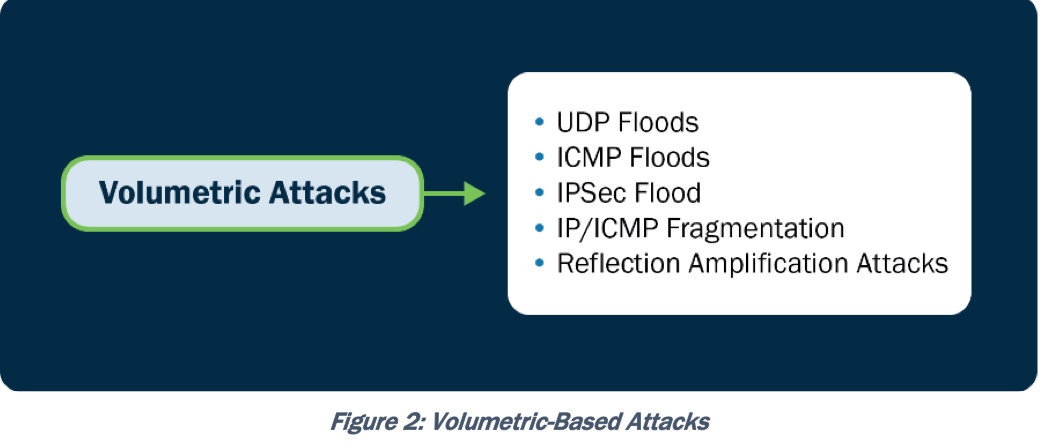
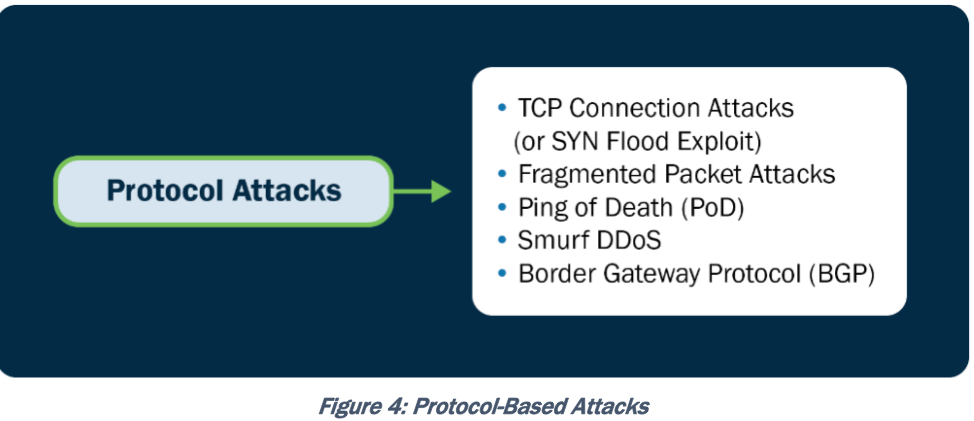
Поэтому CISA различает как минимум три DoS сценария (которые зачастую комбинируются) – атаки на полосу пропускания, атаки на сетевые протоколы, атаки на приложения:
-
- Volumetric, attacks aiming to consume available bandwidth. These attacks aim to consume the available bandwidth or system resources of the target by overwhelming it with a massive volume of traffic. The goal is to saturate the network or exhaust the target's resources, rendering it unable to handle legitimate requests. - Protocol, attacks which exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols or services to disrupt the target. By focusing on weak protocol implementations, the malicious actor can degrade the target's performance or cause it to malfunction. Protocol-based DDoS attacks typically target Layers 3 (network layer) and 4 (transport layer) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. - Application, attacks targeting vulnerabilities in specific applications or running services. These attacks target vulnerabilities in specific applications or services running on the target system. Instead of overwhelming the network or system resources, application layer attacks exploit weaknesses in the targeted application, consuming its processing power or causing it to malfunction. Application-based DDoS attacks target Layer 7, the application layer, of the OSI model. These categories are not mutually exclusive, and malicious actors can combine multiple techniques to launch sophisticated DoS and DDoS attacks. Additionally, new attack methods and variations constantly emerge as malicious actors adapt and evolve their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
Volumetric: UDP/ICMP/IPSec Flood, IP/ICMP fragmentation, reflection/amplification
Protocol-Based: TCP connection/Syn flood, fragmented packet, ping of death, smurf, BGP
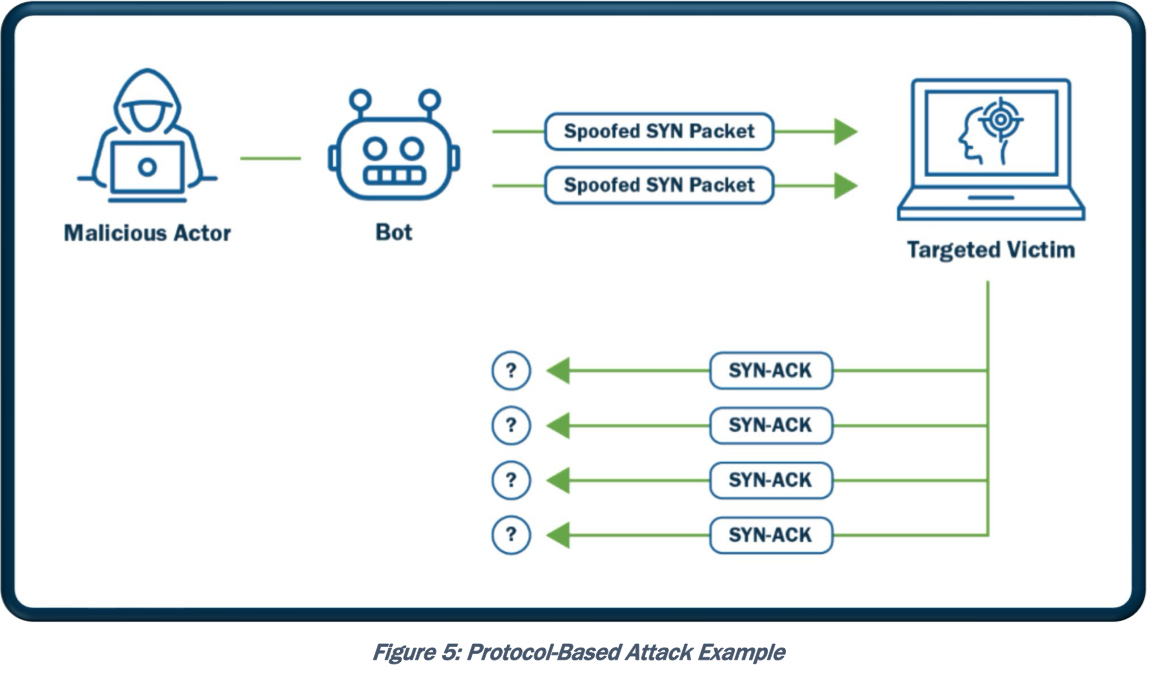
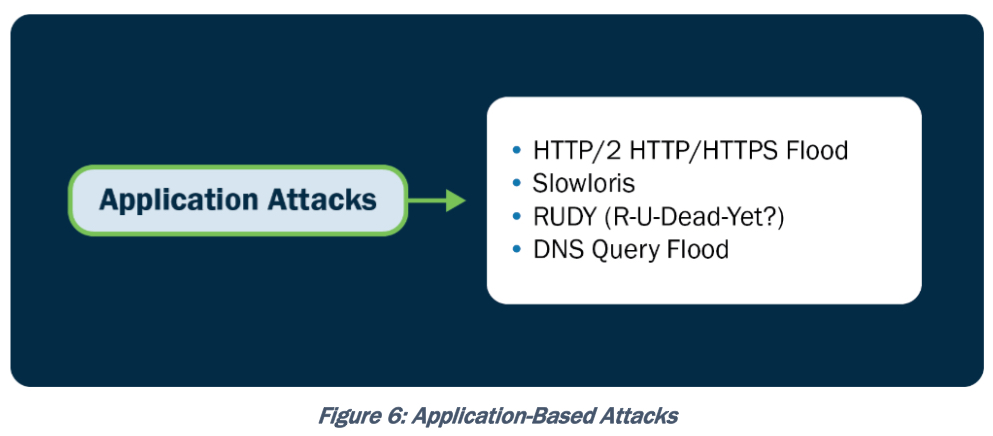
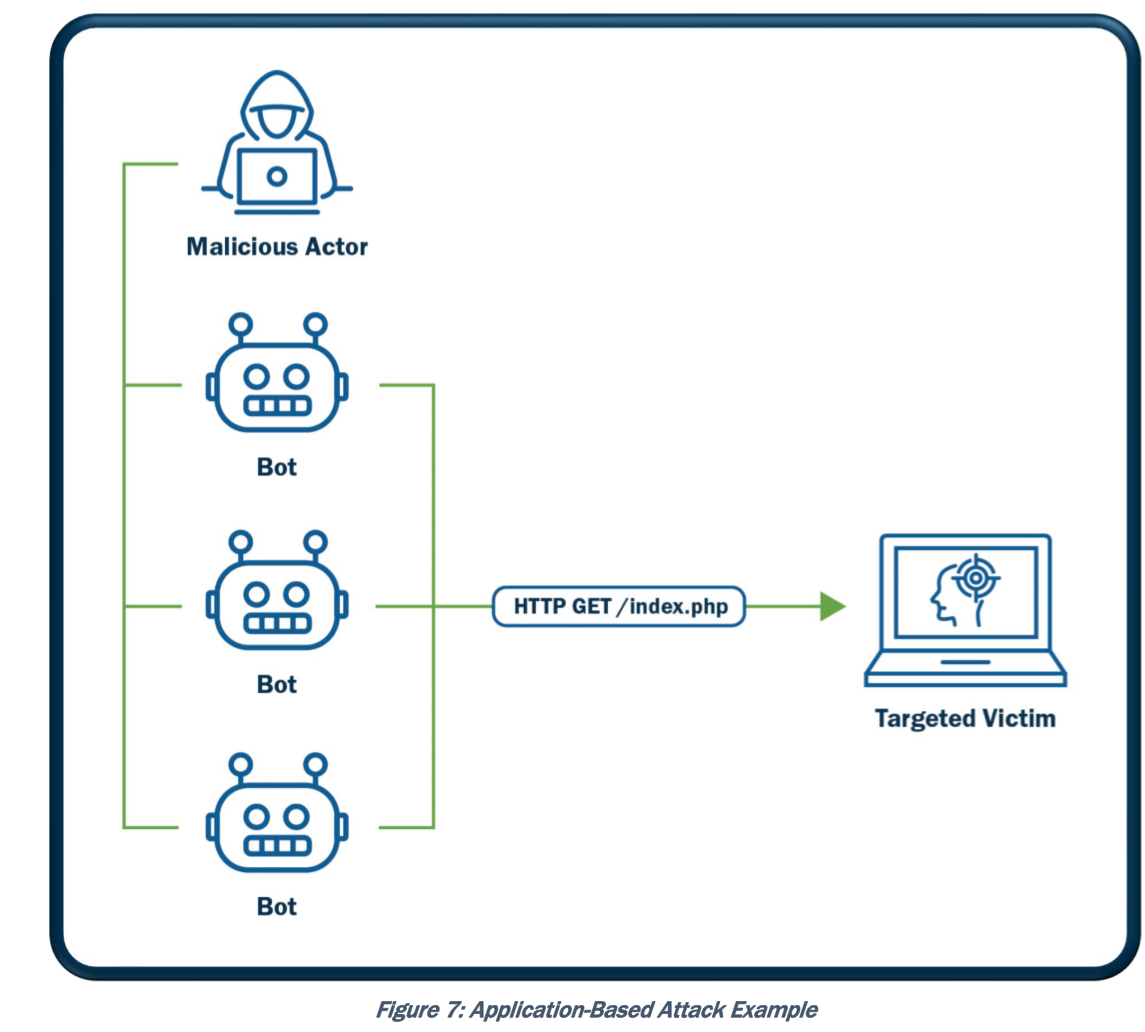
Application Layer-Based Attacks: HTTP(S) flood, slowloris, RUDY, DNS query flood
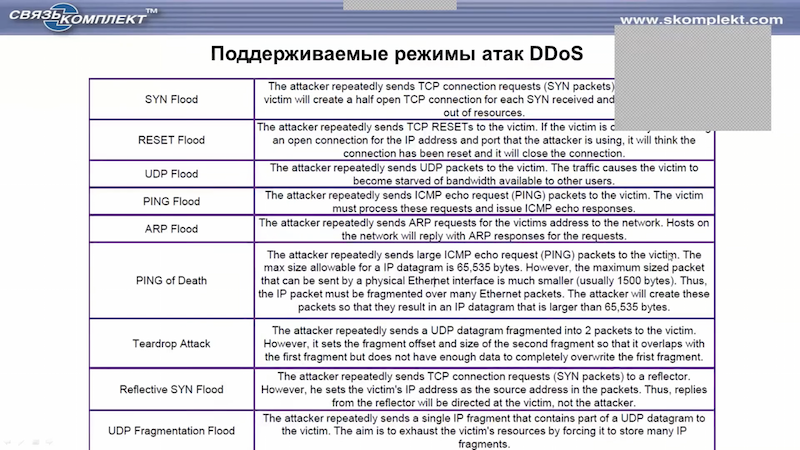
Список поддерживаемых Tera VM DDoS атак (основные атаки).
Существует три основных вида DOS:
-
- Direct (SYN flood) – атакующий отправляет DOS трафик непосредственно жертве (напр. TCP SYN Flood Attack, но, безусловно, он может быть реализован и не напрямую)
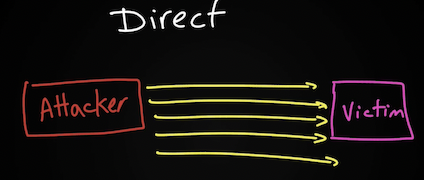
This type of attack is aimed at flooding the victim with an overwhelming number of packets, oversaturating its connection bandwidth, or depleting the target’s system resources. This type of attack is also known as a “SYN flood attack.”
-
-
- Reflected (smurf attack) – атакующий отправляет фейковый трафик (spoofed) на промежуточный хост (или хосты), а промежуточный хост нагружает жертву. Обычно тут используется UDP т.к. его легко подделать (отсутствие 3whs). Примером являются
- smurf атака – когда подменяется адрес источника icmp сообщения на бродкаст адрес и хосты сети начинают отвечать жертве.
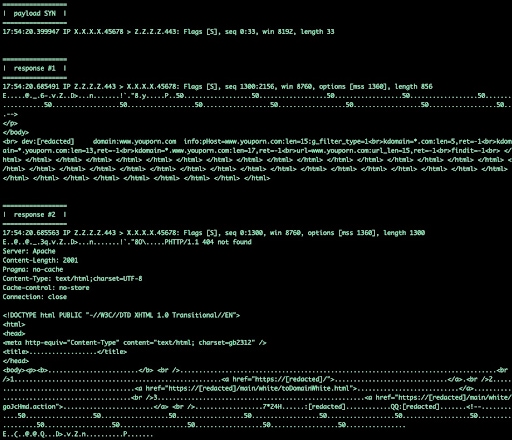
- tcp middlebox reflection – когда используются enterprise или правительственные системы фильтрации (China Great Firewall), которые на один spoofed IP SYN с контентом! (payload SYN) отвечают заблокированным контентом (т.е. без ожидания 3WHS) и как итог, spoofed IP атакуется системами фильтрации. Решения в конце статьи простые (игнорировать SYN + payload, использовать SYN cookies/challenges).
- Reflected (smurf attack) – атакующий отправляет фейковый трафик (spoofed) на промежуточный хост (или хосты), а промежуточный хост нагружает жертву. Обычно тут используется UDP т.к. его легко подделать (отсутствие 3whs). Примером являются
-
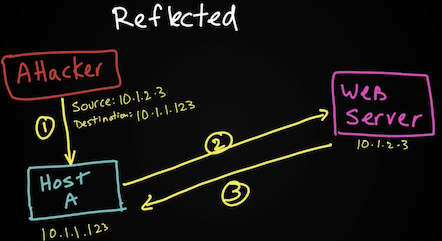
- Reflected DDoS attacks occur when the sources of the attack are sent spoofed packets that appear to be from the victim, and then the sources become unwitting participants in the DDoS attacks by sending the response traffic back to the intended victim. UDP is often used as the transport mechanism because it is more easily spoofed due to the lack of a three-way handshake.
-
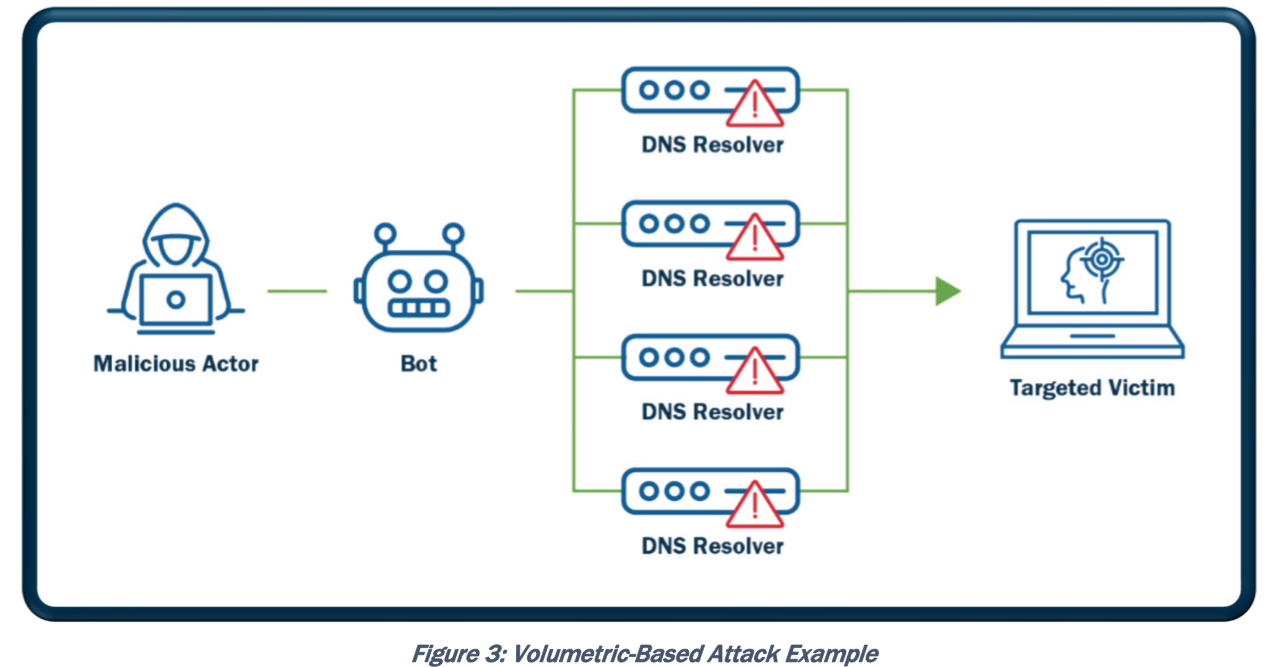
- Amplification (dns amplification attack) – форма reflected атаки, в ней атакующий так же отправляет фейковый трафик (spoofed) на промежуточный хост (или хосты), а промежуточный хост нагружает жертву. В сравнении с классической reflected атакой amplification имеет особенность – промежуточный хост генерирует в итоге большую нагрузку на жертву, чем если бы атакующий передал трафик непосредственно жертве. Пример реализации: используя смену source address мы генерируем на некий сервер небольшой по объему запрос (NTP сервер, DNS сервер и другие сервера), а он отвечает жертве по подмененному SRC адресу большим количеством данных и в результате DDOS’ит его. Так же примером amplification является Smurf amplifier для smurf атаки.
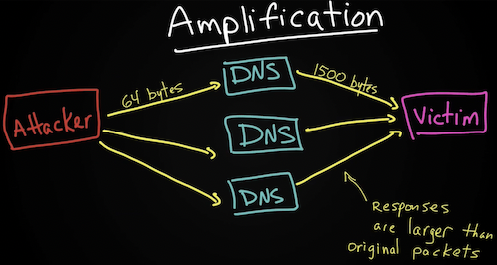
An amplification attack is a form of reflected attack in which the response traffic (sent by the unwitting participant) is made up of packets that are much larger than those that were initially sent by the attacker (spoofing the victim). An example is when DNS queries are sent, and the DNS responses are much larger in packet size than the initial query packets. The end result is that the victim’s machine gets flooded by large packets for which it never actually issued queries.
Формой DoS так же являются buffer overflow атаки (и вообще любые другие атаки), приводящие к отказу сервиса.
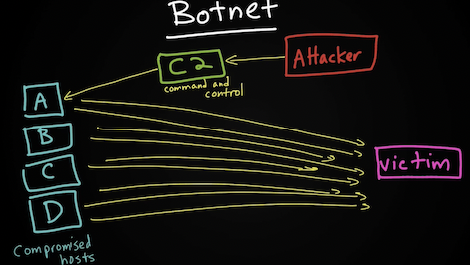
Сегодня большая часть DoS/DDoS атак основана на использовании ботнетов (botnet) с использованием command-and-control серверов (C2, CnC), тогда как ранее на тулзках вроде Ping of Death, Teardrop. Новые ботнеты так же замещают старые (напр. Storm, Mariposa).
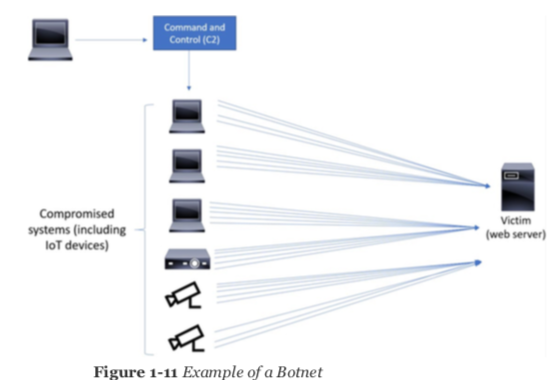
Another type of DoS is caused by exploiting vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows to cause a server or even network infrastructure device to crash, subsequently causing a denial-of-service condition. Today, most DoS attacks are launched via botnets, whereas in the past tools such as the Ping of Death or Teardrop may have been used. Like malware, hackers constantly develop new tools so that Storm and Mariposa, for example, are replaced with other, more current threats. Many attackers use botnets to launch DDoS attacks. A botnet is a collection of compromised machines that the attacker can manipulate from a command-and-control (often referred to as a C2 or CnC) system to participate in a DDoS, send spam emails, and perform other illicit activities.In Figure 1-11, the attacker sends instructions to compromised systems. These compromised systems can be end-user machines or IoT devices such as cameras, sensors, and so on.
DOS/DDOS АТАКИ практика
DOS/DDOS защита
- Flood guards – обеспечение защиты от DoS/DDoS. Обычно реализуется на Firewall/Enterprise Router/IPS/IDS, но есть и open source продукты для небольших организаций, например failed2ban (подробнее в статье iptables). Он обнаруживает атаки по общему паттерну (SYN flood/UDP flood), при достижении порога генерируется alert или даже предпринимаются автоматические меры (activation threshold) – напр. блокируется трафик на определенное время.
A flood guard protects against attacks that overwhelm networking resources, like DoS attacks and SYN floods.
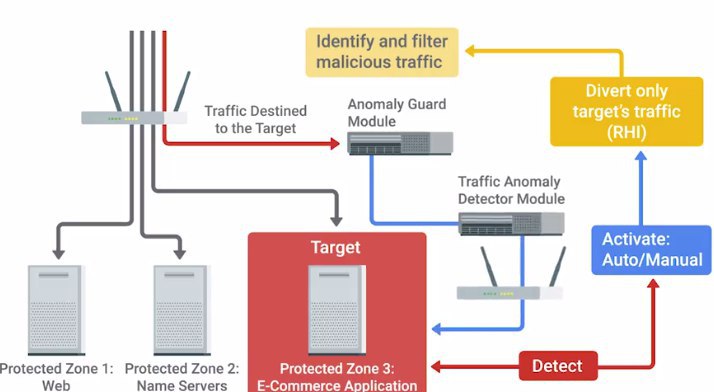
- Почему традиционные Firewall/IPS плохи в защите от DDoS пишут Radware – они имеют серьезные архитектурные ограничения для этого (connection table, only individual session analysis).
The simple answer is that they were not designed to do so. Firewalls and IPS focus on examining and preventing the intrusion of one entity at a time, but were not designed to detect the combined behavior of legitimate packets sent millions of times.
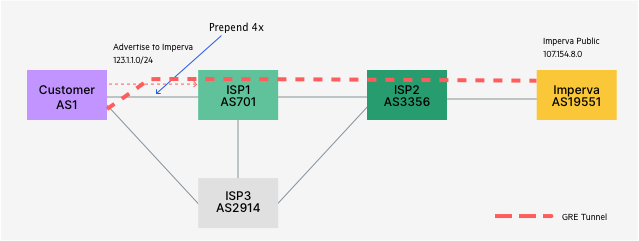
- Пример защиты от DDoS на основе решения от Imperva, так же есть куча альтернатив (напр. de-cix.net, psychz.net и даже Касперский). Работает на основе BGP пиринга поверх GRE через DDoS облако хостера или на основе подмены DNS записи для защищаемого ресурса (DNS lookup резолвит в IP адрес DDoS-хостера). Я решение даже порекомендовал тут в ролике. Трафик к кастомеру маршрутизируется через imperva в результате
- bgp as path prepend
- анонсов конкретных сетей (которых атакуют или потенциально могут атаковать)
- отключением анонсов через основной канал (напр. при атаке)
Я бы на вашем месте "на всякий такой случай" поглядел в сторону связки симка с белым IP + BGP + GRE, если еще не глядели. Буржуи (напр. imperva) предлагают пиринг поверх gre как услугу защиты от ddos, вам же профит будет и в доп. бекапе.
WAF
Web Application Firewall, WAF (cloudflare, incapsula, sucuri) реализует функционал защиты web application от различных атак, включая ddos.
WAF представляет из себя промежуточный (между сервером и клиентов) сервис (сервер/облако), который располагается между клиентом и web application.
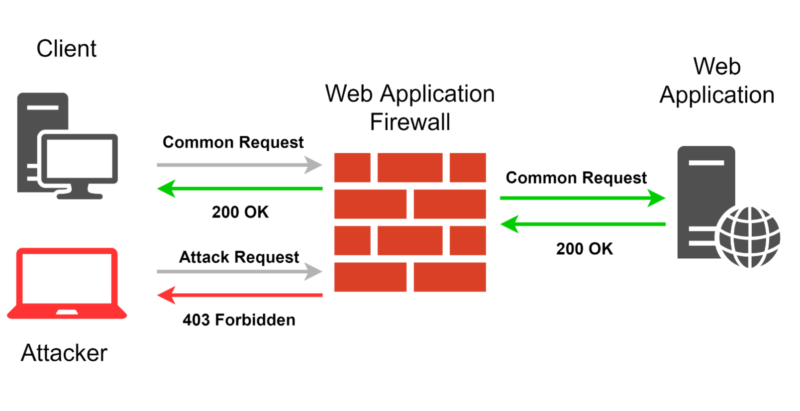
– Клиент резолвит сайт через dns
– Клиент получает один из адресов WAF, а не непосредственно адрес сайта (web application)
– WAF после анализа перенаправляет запрос на web application
– При этом на web application производится настройка приема запросов только от пулов IP WAF – на случай если кто то особо умный из истории dns поднимет твой старый IP.
https://github.com/vincentcox/bypass-firewalls-by-DNS-history Firewall bypass script based on DNS history records. This script will search for DNS A history records and check if the server replies for that domain. Handy for bugbounty hunters. How to protect against this script? If you use a firewall, make sure to accept only traffic coming through the firewall. Deny all traffic coming directly from the internet. For example: Cloudflare has a list of IP's which you can whitelist with iptables or UFW. Deny all other traffic. Make sure that no old servers are still accepting connections and not accessible in the first place
FASTNETMON
FastNetMon - very fast DDoS sensor with sFlow/Netflow/IPFIX/SPAN support. https://www.enog.org/presentations/enog-9/17-FastNetMon_ENOG_pdf.pdf https://github.com/pavel-odintsov/fastnetmon
What we could do? Save NOC’s sleep :) Detect any DoS/DDoS attack for channel overflow or equipment Partially or completely block traffic from/to own host (target of attack) Save your network (routers, switches, servers) Save your SLA
How we could block attack? BGP announce (community 666, blackhole, selective blackhole) BGP flow spec/RFC 5575 (selective traffic blocking) ACL on switch Custom script Attack detection logic By number of packets per second to/from /32 By number of mbps per second from/to /32 By number of flows per second from/to /32 By number of fragmented packets from/to /32 By number of tcp syn packets from/to /32 By number of udp packets from/to /32 Complete support for most popular attacks for channel overflow SYN flood UDP amplification (SSDP, Chargen, DNS, SNMP, NTP) IP fragmentation Performance sFLOW - 40-100GE NetFLOW - 40-100GE Span/mirror - 10-40GE per node (tested up to 10 MPPS) Supported vendors Cisco Juniper Extreme Huawei Linux (ipt_NETFLOW) Example STATS IP: 194.**.**.** Attack type: syn_flood Initial attack power: 516 packets per second Peak attack power: 516 packets per second Attack direction: incoming Attack protocol: tcp Total incoming traffic: 5 mbps Total outgoing traffic: 0 mbps Total incoming pps: 516 packets per second Total outgoing pps: 294 packets per second Total incoming flows: 0 flows per second Total outgoing flows: 0 flows per second Average incoming traffic: 5 mbps Average outgoing traffic: 0 mbps Average incoming pps: 516 packets per second Average outgoing pps: 294 packets per second Average incoming flows: 0 flows per second Average outgoing flows: 0 flows per second Incoming ip fragmented traffic: 0 mbps Outgoing ip fragmented traffic: 0 mbps Incoming ip fragmented pps: 0 packets per second Outgoing ip fragmented pps: 0 packets per second Incoming tcp traffic: 156 mbps Outgoing tcp traffic: 5 mbps Incoming tcp pps: 15013 packets per second Outgoing tcp pps: 8381 packets per second Incoming syn tcp traffic: 155 mbps Outgoing syn tcp traffic: 3 mbps Incoming syn tcp pps: 14590 packets per second Outgoing syn tcp pps: 7733 packets per second Incoming udp traffic: 0 mbps Outgoing udp traffic: 0 mbps Incoming udp pps: 0 packets per second Outgoing udp pps: 0 packets per second Incoming icmp traffic: 0 mbps Outgoing icmp traffic: 0 mbps Incoming icmp pps: 0 packets per second Outgoing icmp pps: 0 packets per second Average packet size for incoming traffic: 1346.9 bytes Average packet size for outgoing traffic: 89.9 bytes Example STATS 2017-01-26 07:44:42,057 [iNFO] Logger initialized! 2017-01-26 07:44:42,058 [WARN] We add subnet 10.10.10.221/32 to host group my_hosts 2017-01-26 07:44:42,058 [WARN] We add subnet 10.10.10.222/32 to host group my_hosts 2017-01-26 07:44:42,058 [iNFO] We have created host group my_hosts with 2 subnets 2017-01-26 07:44:42,058 [iNFO] We will read ban settings for my_hosts 2017-01-26 07:44:42,058 [ERROR] We can't find notify script /usr/local/bin/notify_about_attack.sh 2017-01-26 07:44:42,061 [iNFO] Read configuration file 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] We loaded 5 networks from networks file 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] Totally we have 5 IPv4 subnets 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] Totally we have 0 IPv6 subnets 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] Total number of monitored hosts (total size of all networks): 17920 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] We need 10 MB of memory for storing counters for your networks 2017-01-26 07:44:42,062 [iNFO] I will allocate 4096 records for subnet 2137694 cidr mask: 20 2017-01-26 07:44:42,066 [iNFO] I will allocate 4096 records for subnet 11562416 cidr mask: 20 2017-01-26 07:44:42,069 [iNFO] I will allocate 8192 records for subnet 14708144 cidr mask: 19 2017-01-26 07:44:42,077 [iNFO] I will allocate 1024 records for subnet 9183673 cidr mask: 22 2017-01-26 07:44:42,077 [iNFO] I will allocate 512 records for subnet 2408641 cidr mask: 23 2017-01-26 07:44:42,077 [iNFO] We start total zerofication of counters 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] We finished zerofication 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] We loaded 5 IPv4 subnets to our in-memory list of networks 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] Run banlist cleanup thread, we will awake every 60 seconds 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] netflow plugin started 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] netflow: We will listen on 1 ports 2017-01-26 07:44:42,078 [iNFO] netflow plugin will listen on 10.0.0.20:2055 udp port 2017-01-26 07:44:42,242 [iNFO] Dump: 2017-01-26 07:44:42.240984852 146.66.156.196:27030 > 94.158.37.129:9692 protocol: udp frag: 0 packets: 0 size: 0 bytes ttl: 0 sample ratio: 1 2017-01-26 07:44:42,242 [iNFO] Dump: 2017-01-26 07:44:42.240984852 183.87.48.193:2599 > 193.192.37.3:51413 protocol: tcp flags: - frag: 0 packets: 0 size: 0 bytes ttl: 0 sample ratio: 1 2017-01-26 07:44:42,242 [iNFO] Dump: 2017-01-26 07:44:42.240984852 185.38.12.37:80 > 94.158.32.204:4475 protocol: tcp flags: - frag: 0 packets: 0 size: 0 bytes ttl: 0 sample ratio: 1 2017-01-26 07:44:42,242 [iNFO] Dump: 2017-01-26 07:44:42.240984852 216.147.182.212:31608 > 94.158.35.27:17922 protocol: udp frag: 0 packets: 0 size: 0 bytes ttl: 0 sample ratio: 1 2017-01-26 07:44:42,242 [iNFO] Dump: 2017-01-26 07:44:42.240984852 91.221.248.21:63916 > 94.158.43.45:49412 protocol: udp frag: 0 packets: 0 size: 0 bytes ttl: 0 sample ratio: 1
Cisco IOS/Linux anti-DOS фичи
-
- Защита Control Plane
- COPP/CPPR, подробнее в архитектуре Cisco IOS
- rate-limiting/policing (ниже)
- Защита Control Plane
-
- Защита Connection table
- rate-limiting/policing (ниже)
- есть даже на простейшем роутере ZTE F680:Anti-DoS атакаЗащита от несанкционаированного доступа
“Порог” означает максимальное количество соединений TCP или UDP от одного хоста на стороне WAN к самой CPE каждые 3 секунды. - ограничение на время полуоткрытого соединения <после обнаружения SYN attack> (10 секунд был default) после SYN (SynDefender)
- Защита Connection table
In a SYN attack, the attacker sends many SYN packets without finishing the three-wayhandshake. This causes the attacked host to be unable to accept new connections.You can protect against this attack by specifying a maximum amount of time forcompleting handshakes. A SYN attack is when more than 5 incomplete TCP handshakes aredetected within 10 seconds.
-
-
- Context-Based Access Control (CBAC) – правим таймауты на аномальные состояния, отслеживаем их количество. Аналогичное можно сделать и в conntrack (пример ниже). Подробнее про конкретные таймауты/таймеры читаем тут.
-
Router(config)# ip inspect tcp synwait-time seconds Router(config)# ip inspect tcp finwait-time seconds Router(config)# ip inspect tcp idle-time seconds Router(config)# ip inspect udp idle-time seconds Router(config)# ip inspect dns-timeout seconds
Router(config)# ip inspect max-incomplete high number Router(config)# ip inspect max-incomplete low number Router(config)# ip inspect one-minute high number Router(config)# ip inspect one-minute low number Router(config)# ip inspect tcp max-incomplete host number
CBAC to restrict the number of half-open sessions, which typically is used to prevent TCP SYN flood attacks. This feature is similar to TCP Intercept, but it can examine TCP as well as UDP and ICMP sessions. Of course, with UDP and ICMP, because there is no state machine that defines the setup, maintenance, and removal of a connection, CBAC uses timers instead of connection threshold values.
In this article I will give an example of optimizing the parameters of nf_conntrack for a high-loaded NAT server. On high-load servers, it is desirable to slightly reduce the timeout values, especially during DDOS attacks, or disable nf_conntrack if it is not needed and the server is not used for NAT, for example, change some timeout to such values (I left the uncommented lines unchanged): net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_generic_timeout=60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_icmp_timeout=10 #net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close=10 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait=20 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established=1800 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait=30 # tcp_fin_timeout (default 60, recommended below 10) #net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_last_ack=30 #net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_max_retrans=300 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv=30 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent=60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait=60 #net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_unacknowledged=300 #net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_udp_timeout=30 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_udp_timeout_stream=60
-
-
- tcp_max_tw_buckets – ограничение по количеству сессий (sockets) в состоянии time-wait
-
Specifies the maximum number of sockets in the “time-wait” state allowed to exist at any time. If the maximum value is exceeded, sockets in the “time-wait” state are immediately destroyed and a warning is displayed. This setting exists to thwart certain types of “Denial of Service” attacks. # sysctl -a | grep tcp_max_tw_buckets net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 32768
-
-
- tcp_no_metrics_save – по умолчанию 0 (сохраняем метрики при разрыве соединений, чтобы ускорить новые соединения), рекомендуется 1 (не сохраняем метрики).
- tcp syncookies (cookies) – не создаем соединение на базе SYN пакета, но отсылает SYN+ACK. Если от клиента будет получен в последующем ACK на отосланный SYN+ACK (т.е. получен пакет завершения 3whs) – то создаем соединение. Особенность, что в SYN+ACK в sequence number вкладывается не рандомное значение, а значение на основе адресов в socket + со временем отправки SYN+ACK + значением MSS клиента. В итоге инициировать соединение кто-то кроме отправившего SYN не сможет, так же клиент не сможет инициировать соединение, если превышен таймаут (дефолт 64 секунды). У syncookies есть недостатки, подробнее в WIKI, в вкратце – игнорирование всех TCP опций т.к. они передаются в SYN.
-
/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_syncookies net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies
-
-
- tcp intercept (в активном режиме или watch режиме) – являемся proxy для создаваемых соединений и отслеживаем их. Принцип защиты от SYN flood в таком случае простой – мы пересогласовываем TCP handshake со внутренним сегментом только после получения ACK от клиента (SYN – SYN-ACK – ACK). Недостаток этого подхода – меняются sequence номера и поэтому ассиметричный роутинг перестает работать – т.е. трафик должен форвардится или через одну железку или через кластер, но никак не через независимые железки.
-
The TCP intercept software intercepts TCP synchronization (SYN) packets from clients to servers that match an extended access list. The software establishes a connection with the client on behalf of the destination server, and if successful, establishes the connection with the server on behalf of the client and knits the two half-connections together transparently. Thus, connection attempts from unreachable hosts will never reach the server. The software continues to intercept and forward packets throughout the duration of the connection. The number of SYNs per second and the number of concurrent connections proxied depends on the platform, memory, processor, and other factors
Router(config)# access-list 100 tcp permit tcp any host 192.1.1.1 eq 80 Router(config)# access-list 100 tcp permit tcp any host 192.1.1.2 eq 25 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept list 100 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept mode watch Router(config)# ip tcp intercept watch-timeout 20 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept connection-timeout 120 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept max-incomplete high 600 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept min-incomplete low 500 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept one-minute high 800 Router(config)# ip tcp intercept one-minute low 600
-
- ограничение по количеству non-tcp connections (Non-TCP Flooding, CheckPoint)
Advanced firewalls maintain state information about connections in a State table. In Non-TCP Flooding attacks, the attacker sends high volumes of non-TCP traffic. Since suchtraffic is connectionless, the related state information cannot be cleared or reset, and thefirewall State table is quickly filled up. This prevents the firewall from accepting newconnections and results in a Denial of Service (DoS).You can protect against Non-TCP Flooding attacks by limiting the percentage of state tablecapacity used for non-TCP connections.
-
- ограничение на кол-во соединений на destination порт
https://serverfault.com/questions/371763/limit-maximum-incoming-connections-to-a-port-using-iptables Limit maximum incoming connections to a port using iptables You could try --connlimit with the --connlimit-mask option to set a mask of 0. iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport XXY -m connlimit --connlimit-above 5 --connlimit-mask 0 -j REJECT Where XXY is the port that you want to rate-limit connections to.
- Пакетные фильтры
- Rate-limiting/policing (ниже)
- (U)RPF фильтры
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/rp_filter 0 sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=1
-
- LAND атака в которой SRC IP = DST IP (LAND, CheckPoint)
In a LAND attack, the attacker sends a SYN packet, in which the source address and portare the same as the destination (the victim computer). The victim computer then tries toreply to itself and either reboots or crashes.
-
- попакетная проверка (Packet Sanity, CheckSum Verification, Sequence verifier, Strict TCP, Small PMTU; CheckPoint)
- корректность IP/UDP/TCP длин payload,
- опций протоколов (IP options, TCP flags, Sequence, etc)
- out-of-state packets (Strict TCP; assymetric routing, firewall restart)
- small packets (Small PMTU, <300 byte)
- checksum
- попакетная проверка (Packet Sanity, CheckSum Verification, Sequence verifier, Strict TCP, Small PMTU; CheckPoint)
Packet Sanity performs several Layer 3 and Layer 4 sanity checks. These include verifying packet size, UDP and TCP header lengths, dropping IP options, and verifying the TCPflags. SmartDefense identifies any IP, TCP, or UDP packets with incorrect checksums. You can configure how these packets should be handled. Out-of-state TCP packets are SYN-ACK or data packets that arrive out of order, before theTCP SYN packet. Note: In normal conditions, out-of-state TCP packets can occur after the UTM-1restarts, since connections which were established prior to the reboot are unknown.This is normal and does not indicate an attack. Small PMTU (Packet MTU) is a bandwidth attack in which the client fools the server intosending large amounts of data using small packets. Each packet has a large overhead thatcreates a "bottleneck" on the server.You can protect against this attack by specifying a minimum packet size for data sent overthe Internet.
-
- фильтр по размеру пакетов PING (Max Ping Size, CheckPoint)
An attacker can echo the client with a large amount of data, causing a buffer overflow.You can protect against such attacks by limiting the allowed size for ICMP echo requests
-
- фильтр фрагментированных пакетов с настройками размеров пакетов, количество времени перед дропов и максимального размера очереди (IP fragments, Ping of Death, Teardrop; CheckPoint)
Rate-liminiting/policing
Rate-limiting – делаем порог по количеству трафика определенных подсетей/протоколов и проч.
Router(config)# interface vlan10 Router(config-if)# rate-limit input access-group rate-limit 199 256000 64000 64000 conform-action transmit exceed-action drop
Network quota – делаем порог в 100 CPS rate (default value) для SRC IP (Network quota, CheckPoint).
An attacker may try to overload a server in your network by establishing a very large number of connections per second. To protect against Denial Of Service (DoS) attacks, Network Quota enforces a limit upon the number of connections per second that are allowed from the same source IP address.
Сетевое нагрузочное тестирование DoS
-
- Radware DefensePro 1006 v6.12.01
- Arbor Networks APS 2800 v5.8.1 – Street Price $175,000
- Corero SmartWall v8.10.248 – Street Price $160,000
- F5 BIG-IP 10250v v12.0.0
- Fortinet FortiDDoS 2000B v4.1.10
- Huawei AntiDDoS8030 V500R001C00SPC600
Забавная ситуация, что Arbor не предоставил данные о GPL стоимости.
Arbor Networks declined to provide list pricing for the device tested.
-
- Автоматически обнаруживать и блокировать все категории DDoS атак при том, что используется один subnet для легитимного и нелегитимного трафика – т.е. базовый фильтр по IP не поможет
- Быть устойчивыми к evasion
- Предоставлять “reasonable” доступ к защищаемым ресурсам во время атаки: критерием успешности (того, что тест пройден) является
- отсутствие блокировки легитимного трафика с нагрузкой в 40% от заявленной производительности
- полная блокировка атак
- т.е. атак до 60%, 40% под легитимный трафик
Так же про DoS тестирования можно найти информацию в Ixia Black Book DoS/DDoS testing. Измеряется тоже самое – обнаружение и блокирование, влияние на легитимный трафик.
Attack Mitigation Score Baseline Impact Score Testing mitigation strategy and impact in QoE of users
-
- Test Case: Application Forwarding Performance Under DoS Attacks
- Test Case: Mitigation of TCP SYN DDoS attack/ICMP Fragments/SIP invite flood/MIX/etc.etc.etc
Тестирование DDoS с использованием Ixia BreakingPoint (ее использовали и NSS Labs).
Наиболее интересное из методики и отчетов NSS Labs.
- Both the legitimate network traffic and the DDoS attack are executed using a shared pool of IP addresses, which represents a worst-case scenario for the enterprise. Since legitimate traffic uses the same IP addresses as the attacker, no product can simply block or blacklist a range of IP addresses. This test can reveal the DUT’s true ability to effectively mitigate attacks. ((спорный пункт про один конкретный IP - как часто DoS и легитимные запросы могут передаваться с одного хоста - ответ нечасто, даже аналитику проводить не надо для этого.)) - NSS analysis is conducted first by testing every category of DDoS attack individually to determine that the DUT can successfully detect and mitigate each attack. Once a baseline of security effectiveness is determined, NSS build upon this baseline by adding multiple DDoS attacks from different categories in an attempt to overwhelm the DUT and allow “attack leakage” to occur. At each point during testing, NSS validates that legitimate traffic is still allowed and is not inadvertently blocked by the DUT. - In all security effectiveness tests, a mix of http traffic is run to establish a baseline of legitimate traffic. This traffic is run at 40% of the device’s rated bandwidth, and is used to ensure that legitimate traffic is not affected during mitigation. The baseline impact percentage is listed as the amount of baseline traffic that is affected by the device while the device is mitigating an attack. As an example, if the baseline impact score is 5%, then 5% of the known baseline traffic was inadvertently blocked during attack mitigation. - After the baseline traffic has been stabilized at 40% of the rated bandwidth, an attack is started. These attacks are intended to saturate the network link in terms of either bandwidth or packet rate. To calculate the percentage of each attack that is being mitigated, the known amount of attack traffic being injected into the device is compared with the amount of attack traffic that is allowed to pass through the device. This percentage is calculated separately from the baseline impact score, which allows for a scenario where a device may mitigate an attack very well, but at the same time cause an unintended impact to legitimate services. - During NSS testing, vendors tune their devices to create a performance baseline based on normalized network traffic. Devices are further tuned for accuracy as needed. The performance baseline traffic is 40% of rated throughput and consists of a mix of web application traffic to provide readers with relevant security effectiveness and performance dimensions based on their expected usage.
Специализированные решения длля защиты от (D)DoS.
-
- Radware DefensePro 1006 v6.12.01
- Arbor Networks APS 2800 v5.8.1 – Street Price $175,000
- Corero SmartWall v8.10.248 – Street Price $160,000
- F5 BIG-IP 10250v v12.0.0
- Fortinet FortiDDoS 2000B v4.1.10
- Huawei AntiDDoS8030 V500R001C00SPC600
Партнерство Cisco с Arbor и Radware
Насколько DDoS – это специфика, что даже Cisco, будучи ключевым вендором в телекоммуникационной индустрии использует партнерство с вендорами (arbor, radware), которые разбираются в DDoS (и имеют патенты, что, возможно, ключевое), для реализации функционала защиты от DDoS в своих ключевых Service Provider и Security продуктах.
- В ASR9000 добавлен функционал защиты от DDoS на базе Arbor
- В старшие FirePower добавлен функционал DDoS mitigation от Radware Virtual DefensePro (vDP)
Решение на базе Arbor
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/asr-9000-series-aggregation-services-routers/solution-overview-c22-736143.html https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/asr-9000-series-aggregation-services-routers/datasheet-c78-736894.html
- требует установленную карту Virtualized Services Module, VSM
- отправляет метаданные в коллектор Arbor SP (деплоится в VM in-house)
NetFlow to Arbor Networks Peakflow SP - получает сигнатуры с актуальными ботнетами/правилами из облака Arbor
ATLAS Both Peakflow and vDDoS protection receive regular updates from the Arbor Networks ATLAS Intelligence Feed (AIF), informing the device about the latest and most relevant DDoS threats from botnets and other sources.
Решение Radware Virtual DefensePro
- DDoS prevention solutions … can be integrated into NGFW.
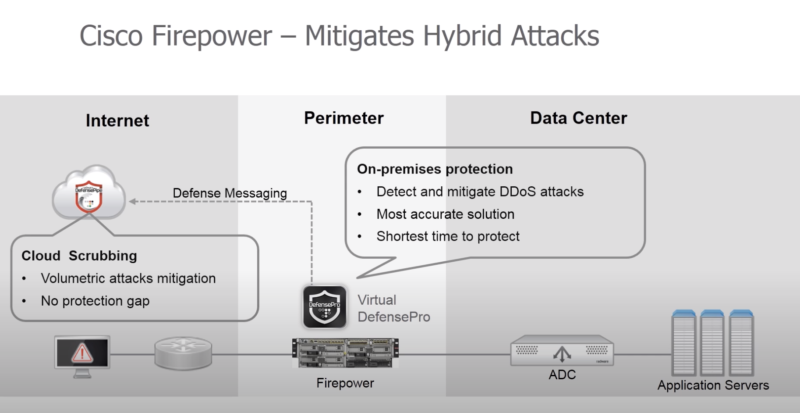
- представляет собой судя по всему VM, устанавливаемую на одну аппаратную платформу с FirePower
- отправляет профиль трафика (netflow) в облачный сервис Radware для анализа
- делает выводы не только на основе spike нагрузок (в radware называют это legacy rate based solutions), но и анализируя поля в пакетах (напр. распределение по SYN, RST флагам в TCP)
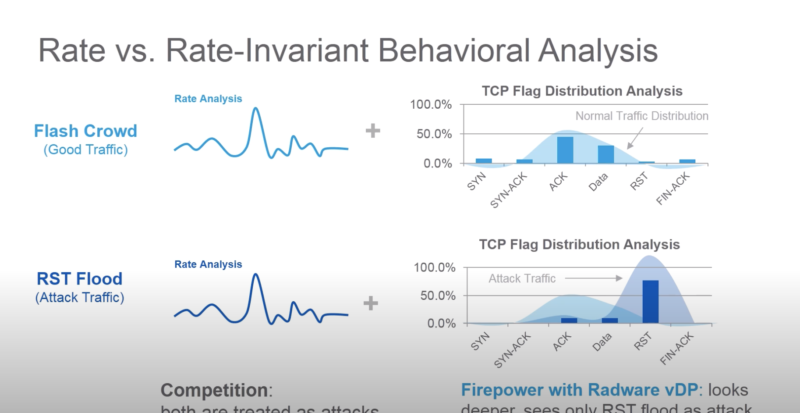
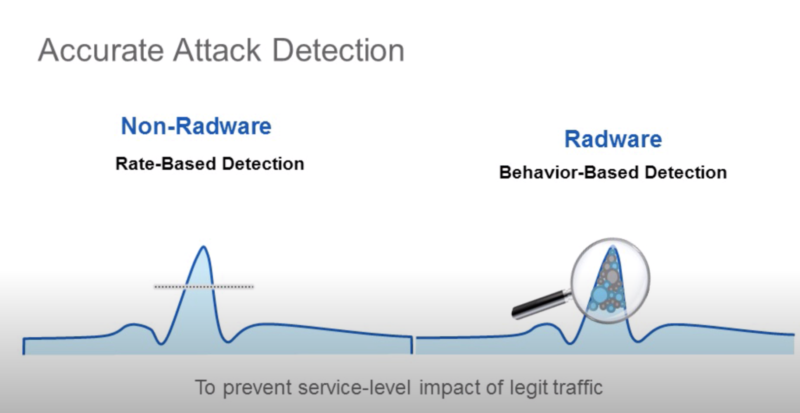
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aOLM9md2eMQ https://www.radware.com/partners/cisco/firepower-ngfw/ Firepower DDoS Mitigation Also available on the Cisco Firepower 4100 Series and 9300 appliances is tightly integrated, comprehensive, behavioral DDoS mitigation for both network and application infrastructure protection. This DDoS mitigation is Radware’s Virtual DefensePro (vDP). It is available from and supported directly by Cisco.
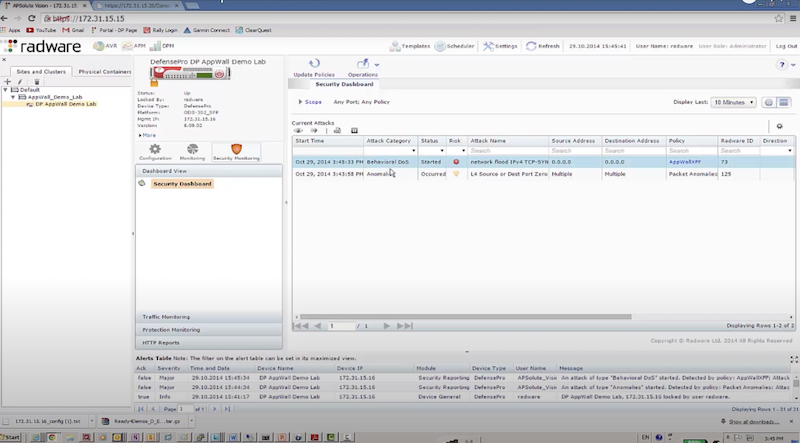
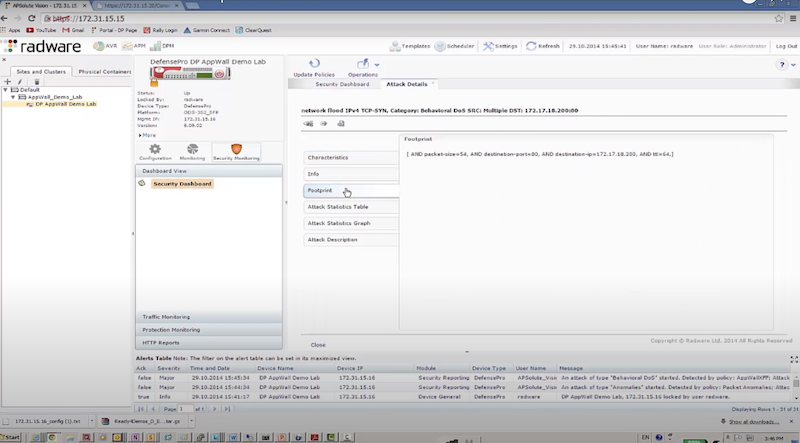
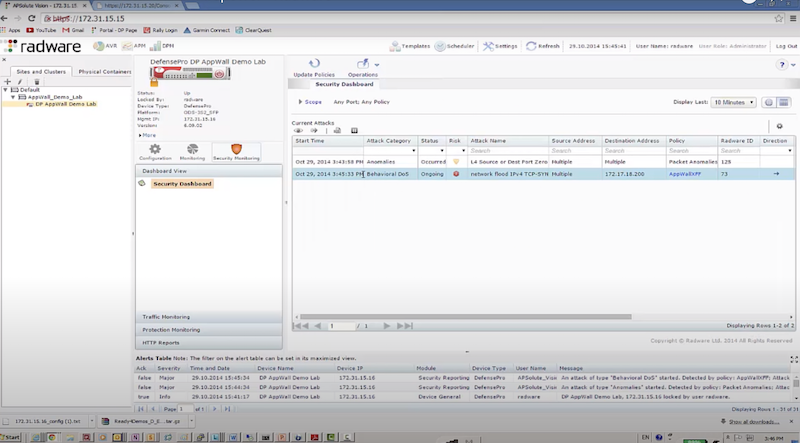
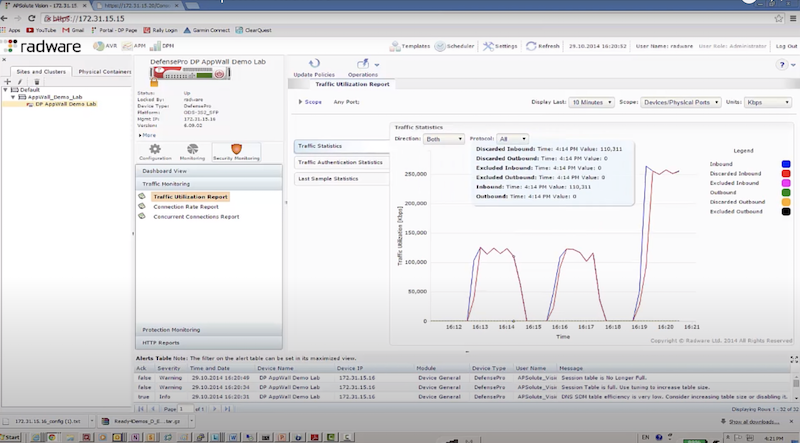
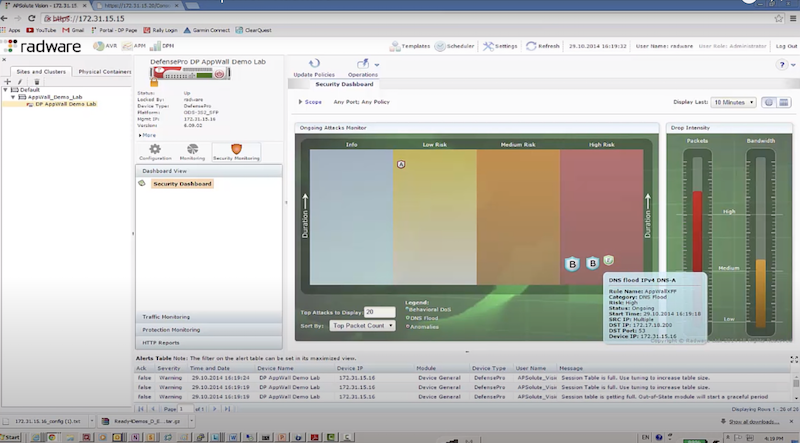
Пример защиты:
- отправляем TCP syn flood с использованием hping3 – radware успешно блокирует атакующие пакеты к dst на основе acl: packet size, ttl, destination IP, destination port
hping3 172.17.18.200 -S -p 80 --rand-source --flood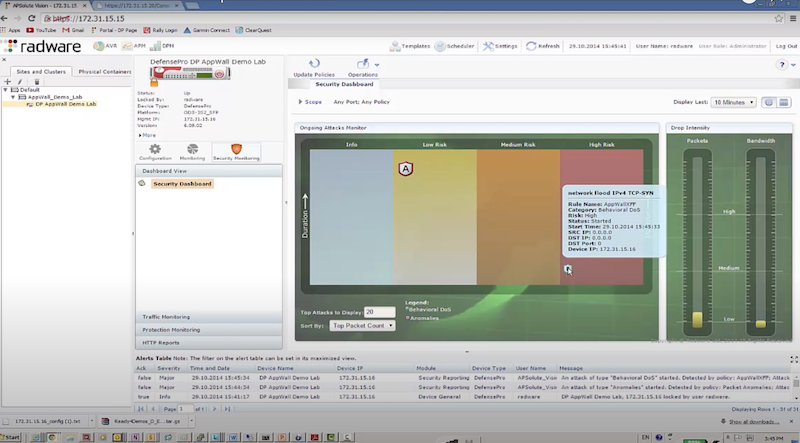
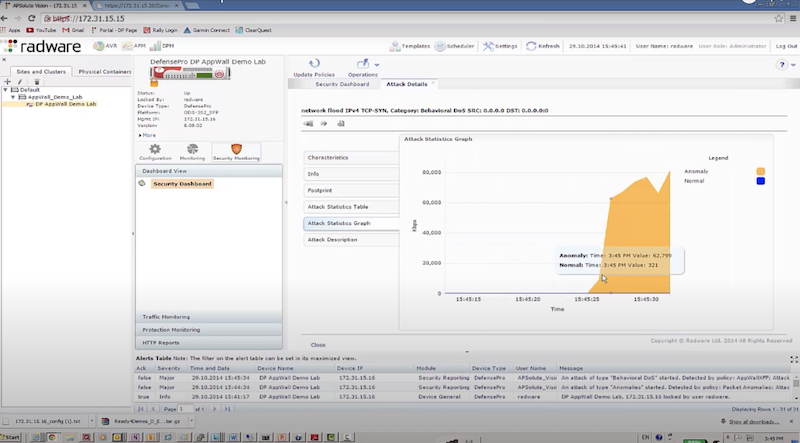
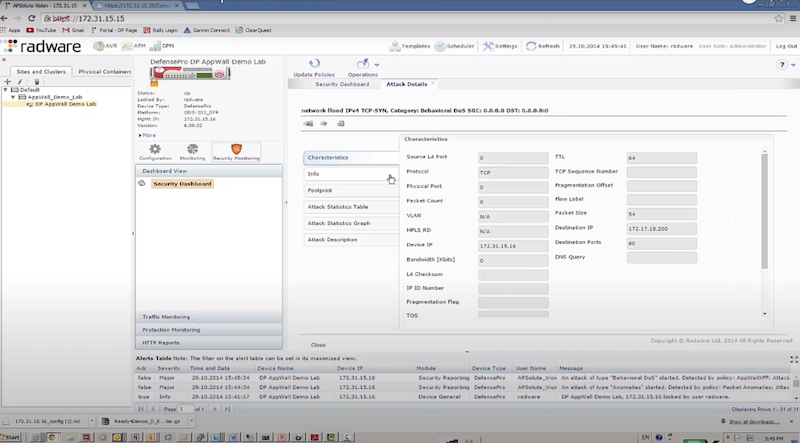
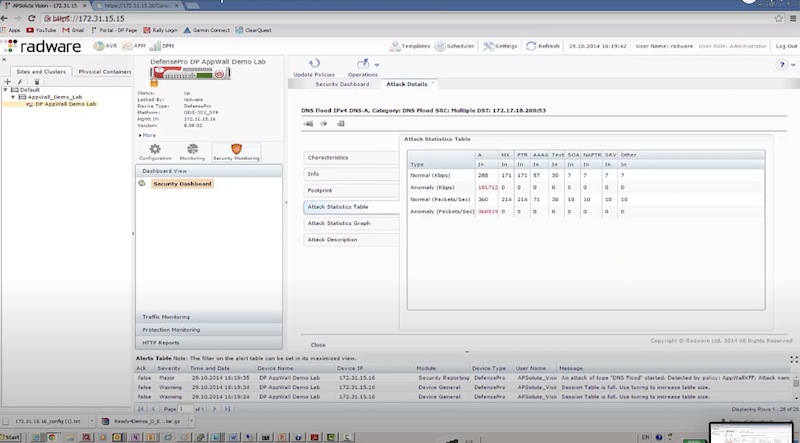
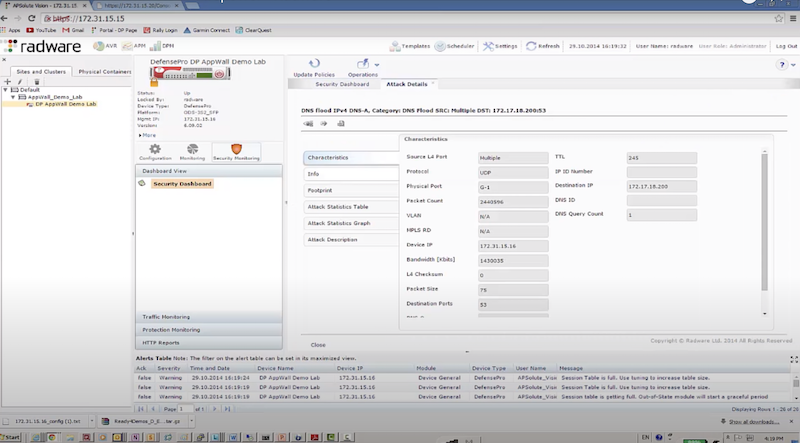
- отправляем DNS flood с использованием dns-flood – radware успешно блокирует атакующие пакеты к dst на основе acl: in probe dns query to attack destination
./dnsflood www.radware.com 172.17.18.200 -t A -r -p 53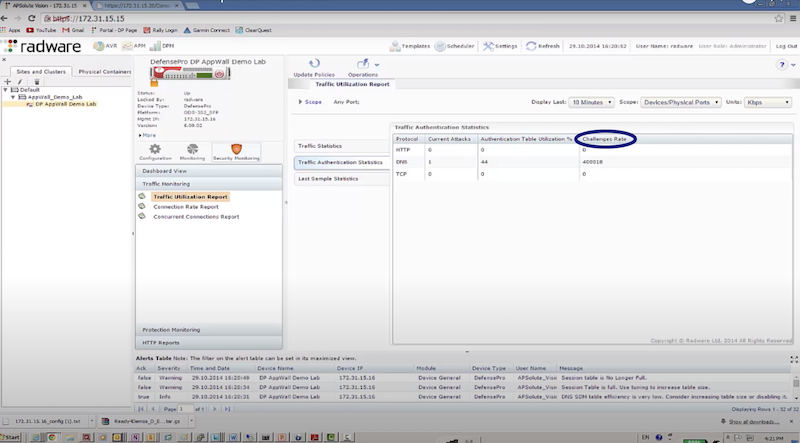
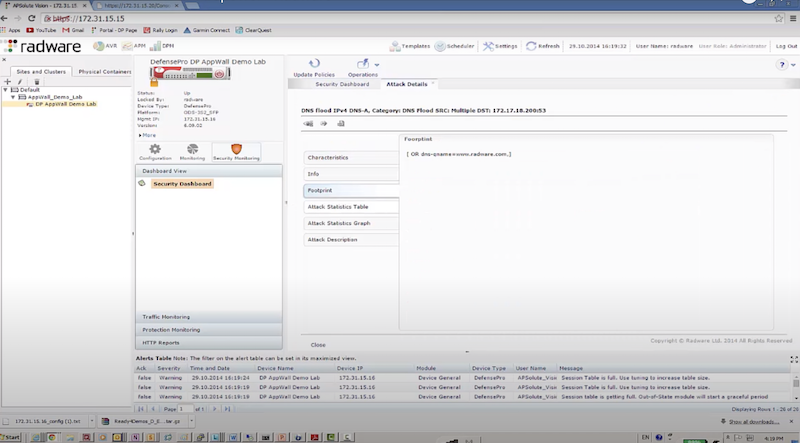
Qrator Labs
Молодцы.
https://www.arista.com/assets/data/pdf/CaseStudies/Qrator_CaseStudy.pdf Project Background In 2006 Alexander Lyamin, then a staff member at the Moscow State University, began a research initiative focused on the problems presented by Distributed Denial of Service attacks. For several years his team studied the mechanics of DDoS attacks and developed algorithms and measures that would allow users to counter these potentially devastating threats effectively. By early 2009, the team had created a specialized application capable of automatic attack detection and filtering. To field-test the algorithms and hardware they developed, Lyamin released an open beta of the product. For 18 months, anyone vulnerable to DDoS attacks could test-drive the technology at no charge, and over that period more than 600 companies and individuals took advantage of this opportunity, allowing Lyamin and his developers to assess the efficacy of the application in actual DDoS attacks, collect unique statistics, and fine-tune algorithms. In 2009, Lyamin founded Qrator Labs, turning a highly innovative research project into a successful commercial DDoS mitigation cloud which is today one of the largest services of its kind in Eastern Europe, providing protection for organizations in financial services, media, gaming, government and many other areas.
Из интересного – используют BGP flowspec для инъектов маршрутов в таблицы провайдеров, которые позволяют блокировать трафик. Причем в случае Arista они, т.к. Arista BGP не умеет, поставили на нее сами демон ExaBGP, который анонсирует необходимые маршруты с flowspec аплинкам.
For the Qrator service to operate at optimum efficiency, it needed to manage BGP flow spec, an extension to the BGP protocol that allows the transfer of the firewall filter rules from one machine to another using BGP protocol. Although the Arista switch did not support the BGP daemon required, the open nature of the Arista EOS architecture meant that Qrator could install a third-party daemon - ExaBGP for flowspec injection, into its uplinks. Qrator has added a number of additional applications and extensions directly into the Arista switch to enhance the functionality of its DDoS services. With the custom created daemons and Qrator software running within each switch, the service is also able to deliver the custom telemetry it needs to identify and block DDoS attacks. когда делали блэкхол - наши операторы Flow spec не умели, да и exabgp тоже :) Сейчас выглядит достаточно простым в реализации (пути относительно репы на github'е): - exabgp/qa/conf/api-flow.run - exabgp/qa/conf/api-flow.conf https://rascom.ru/include/bgpFlowSpec1_ru.pdf С апреля 2016 в РАСКОМ (AS20764) введен в эксплуатацию инструмент защиты от DDOS - flowspec, управляемый из личного кабинета в том числе! С мониторингом и статистикой. https://www.rascom.ru/
Все приходит к Whitelisting – рарешать только легитимный трафик-антиддос. Потому что паразитных паттернов бесконечность, в отличии от легитимных.
Рекомендации организациям по мерам предотвращения/подготовки к DoS/DDoS от Cisa
Переводить лень, в целом достаточно все очевидно
What Steps Should Your Organization Take Before Experiencing a DDoS Attack? No organization can predict when a DDoS attack will occur. However, malicious actors often look for gaps in security systems to launch a DDoS attack; therefore, it is imperative that an organization's network defenders implement best practices to minimize the potential damage of a DDoS attack. The following is a list of proactive DDoS steps to consider: 1. Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough and proactive risk assessment to determine your organizations vulnerability to DDoS attacks. Risk assessments can identify potential vulnerabilities in your network infrastructure, systems, and applications. Such an assessment will also help your organization understand the potential impact of a DDoS attack and aid in prioritizing and implementing appropriate security measures. 2. Network Monitoring: Implement robust network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to identify any unusual or suspicious traffic patterns. This can heighten your organization's ability to detect and respond to DDoS attacks. 3. Traffic Analysis: Regularly analyze your network traffic to establish a baseline of normal traffic patterns. This helps you identify any significant deviations during an attack. 4. Implement Captcha: Integrating a Captcha challenge into a website or online service to help differentiate between human users and automated bots, which helps prevent DDoS attacks. By requiring human interaction to access or interact with websites, Captcha acts as preventive barrier against DDoS attacks. 5. Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a DDoS attack. The plan should include roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and predefined mitigation strategies. 6. DDoS Mitigation Service: Consider employing the services of a DDoS mitigation provider. They possess the expertise and specialized infrastructure to handle large-scale attacks and can help filter out malicious traffic before it reaches your network. 7. Bandwidth Capacity Planning: Evaluate your current bandwidth capacity and consider increasing it to handle sudden spikes in traffic during an attack. This can help minimize the impact on legitimate users. 8. Load Balancing: Implement load balancing solutions to distribute traffic across multiple servers or data centers. This can help distribute the load and prevent a single point of failure during an attack. 9. Firewall Configuration: Configure your firewalls to filter out suspicious traffic patterns and/or block traffic from known malicious IP addresses. Keep the firewall rules updated and consider implementing rate limitations to prevent overwhelming traffic. 10. Patch and Update Systems: Regularly update and patch all software, operating systems, and network devices to address known vulnerabilities. Vulnerable systems can be exploited to amplify the impact of a DDoS attack. 11. Web Application Security: Implement secure coding practices and conduct regular security assessments of your web applications. Vulnerable applications can be targeted to exhaust server resources during an attack. 12. Redundancy and Failover: Implement redundant network infrastructure and ensure failover mechanisms are in place. This will help maintain service availability during an attack by quickly redirecting traffic to alternative resources. 13. Employee Awareness and Training: Educate employees about DDoS attacks, their impact, and how to recognize and report suspicious activities. This will help minimize the risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks that can aid in launching a DDoS attack. 14. Communication Plan: Develop a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed during an attack. This includes internal teams, customers, and third-party service providers. Clear communication helps manage expectations and coordinates response efforts. 15. Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data and ensure you have a tested and updated disaster recovery plan. This will help you recover quickly after an attack and minimize potential data loss. Note: These steps can help mitigate the impact of a DDoS attack, it's crucial for organizations to remain vigilant to these types of attacks and remain in constant communication with their organization cybersecurity professionals and stay updated on the latest security practices to effectively defend against evolving threats.
Рекомендации организациям как понять, что вы находитесь под DoS/DDoS атакой
Аналогично
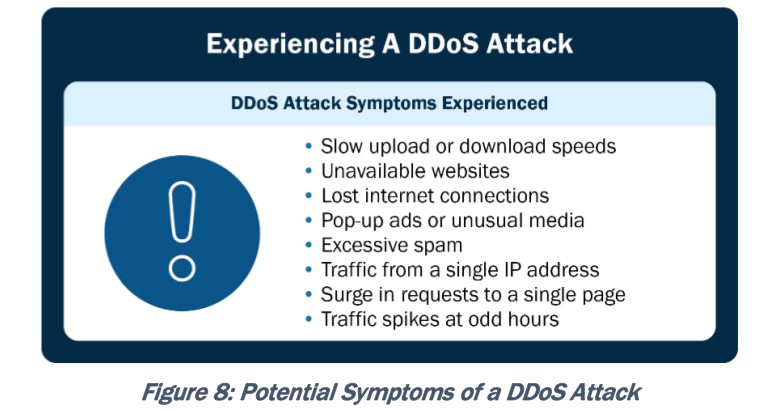
How Does Your Organization Know If It's Experiencing a DDoS Attack? Identifying whether your organizations is experiencing a DDoS attack can be challenging, as symptoms can vary depending on the attack type and intensity. The following is a wide-ranging list to help network defenders determine if there is a DDoS attack occurring: 1. Website or Service Unavailability: The most common symptom of a DDoS attack is the unavailability of a website or online service. If a website suddenly becomes inaccessible or experiences significant slowdowns, it could be a sign of a DDoS attack. 2. Network Congestion: If there is a sudden increase in network traffic or congestion, it may indicate a DDoS attack. Network monitoring tools, or bandwidth usage reports can help identify abnormal spikes in traffic. 3. Unusual Traffic Patterns: Look for unusual traffic patterns in network logs or monitoring systems. This can include a significant increase in requests from specific IP addresses or a high volume of traffic targeting a specific resource or URL. 4. Server or Application Crashes: DDoS attacks can overwhelm your servers or applications, leading to crashes or unresponsiveness. If networks suffer from frequent server or application failures without an apparent reason, it could be a sign of an attack. 5. High Resource Utilization: Monitor server and network resource utilization metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, or bandwidth usage. A sudden and sustained increase in resource consumption may indicate a DDoS attack. 6. Inability To Access Other Network Services: Websites or services may not be the only target of a DDoS attack, other critical network infrastructure components (such as DNS servers or firewalls) may also be at risk. If there are difficulties associated with accessing these services, it could be a sign of an attack. 7. Anomalies in User Behavior: Monitor user behavior on your website or service. If there is a significant increase in the number of requests from a single IP address or unusual patterns, it may be a sign of a DDoS attack. 8. Flood of Spam or Malicious Emails: DDoS attacks can be launched in conjunction with other types of attacks, such as email spam campaigns. If there is a sudden surge in spam or malicious emails originating from organizational networks, it could be part of a coordinated DDoS attack. 9. Notifications From DDoS Protection Service: If you have engaged a DDoS protection service, they may proactively alert you if they detect an ongoing attack on your network. 10. Communication Disruptions: DDoS attacks can target communication channels, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services or messaging platforms. If there are disruptions or quality degradation in network communication services, it may be an indication of an attack.
Как отражать DoS атаки (с учетом что вы готовились 😁) от CISa
How Organizations Can Respond to a DDoS Incident
Organizations experiencing a DDoS attack, are encouraged to initiate incident response plans, contact DDoS protection service provider (if applicable), and engage with your network security team to mitigate the attack and restore normal operations. The following is a list of steps to consider:
1. Identify the Attack: Recognize the signs of a DDoS attack, such as a sudden surge in traffic, increased network latency, or unavailability of services. Use network monitoring tools and traffic analysis to confirm the attack.
2. Activate Incident Response Plan: Implement your organization's documented and approved incident response plan immediately. This plan should outline the roles and responsibilities of key personnel, communication channels, and the steps to be taken during a DDoS attack.
3. Notify Service Providers: Contact internet service providers (ISP) or hosting providers to inform them about the attack. They may have mitigation measures in place or be able to reroute traffic to help mitigate the impact.
4. Gather Evidence: Document and collect as much information as possible about the attack, including timestamps, IP addresses, packet captures, and any logs or alerts generated by your network infrastructure. This evidence can be useful for reporting the incident to law enforcement agencies or for future analysis.
5. Implement Traffic Filtering: Configure network infrastructure, firewalls, or intrusion prevention systems to filter out malicious traffic. Use rate-limitation or access control lists to block traffic from suspicious IP addresses or specific protocols commonly used in DDoS attacks.
6. Enable DDoS Mitigation Services: If available, activate DDoS mitigation services provided by your ISP or third-party vendors specializing in DDoS protection. These services can help filter and divert malicious traffic, allowing legitimate traffic to reach your network.
7. Scale Up Bandwidth and Resources: If your organization has the capacity, consider scaling up your network bandwidth and resources to absorb the attack traffic. This may involve adding additional servers or increasing your network capacity temporarily.
8. Enable Content Delivery Network (CDN): Utilize a CDN service to distribute content across multiple servers and data centers geographically. CDNs can help mitigate DDoS attacks by absorbing and distributing traffic, minimizing the impact on your infrastructure.
9.Communicate Internally and Externally: Maintain clear and regular communication with key stakeholders, including employees, customers, partners, and vendors. Provide updates on the situation, steps taken to mitigate the attack, and expected timelines for resolution.
10. Learn From the Attack: After the situation is resolved, conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to understand the attack vectors, vulnerabilities exposed, and lessons learned. Update your incident response plan and security measures accordingly to prevent future attacks.
11. Use Mitigations Outlined in the MS-ISAC Guide to DDoS Attacks. Immediate mitigations include:
• Provide attacking IP addresses to your ISP. They can implement restrictions to prevent further traffic.
• Keep in mind that reflection DDoS attacks typically originate from legitimate public servers.
• Consider asking your ISP to implement port and packet size filtering.
Note: Every DDoS attack is unique, and the appropriate response may vary based on the nature and severity of the attack. It is advisable to consult cybersecurity professionals or incident response experts to assist your organization in responding to and mitigating DDoS attacks effectively.
Что делать после инцидента (CISO)
так же достаточно очевидно
What Steps Should Your Organization Take If It Has Suffered a DDoS Attack?
If your organization has suffered a DDoS attack, there are several important steps your organization can take to recover and mitigate any potential damages. Here is a list of actions to consider:
1. Assess the Impact: Evaluate the impact of the DDoS attack on your systems, network, and services. Identify any areas of disruption, data loss, or compromised systems. This assessment will help you understand the extent of the damage and prioritize recovery efforts.
2. Restore Services: Restore affected services and systems to normal operations. Depending on the nature of the attack and the systems involved, this may involve restarting servers, reconfiguring network devices, or restoring data from backups. Work closely with your IT teams to ensure a smooth recovery process.
3. Perform a Post-Incident Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the attack to understand its characteristics, vulnerabilities exploited, and attack vectors used. This analysis will help you identify any weaknesses in your infrastructure or security measures and guide future improvements.
4. Implement Remediation Measures: Based on the post-incident analysis, implement remediation measures to address any identified vulnerabilities or weaknesses. This may involve patching systems, updating security configurations, or enhancing network defenses.
5. Review Security Controls: Evaluate existing security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and DDoS mitigation services. Ensure they are properly configured and up to date with the latest threat intelligence. Make any necessary adjustments to enhance your defenses against future attacks.
6. Update Incident Response Plan: Update your incident response plan to incorporate lessons learned from the DDoS attack. Revise roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and mitigation strategies based on the insights gained. This will help in responding more effectively to future incidents.
7. Educate Employees: Provide training and awareness programs for employees to educate them about DDoS attacks, their impact, and how to recognize and report suspicious activities. Enhancing employee awareness can help prevent social engineering attacks and improve overall cybersecurity hygiene.
8. Enhance Network Monitoring: Strengthen your network monitoring capabilities to effectively detect and respond to future DDoS attacks. Implement real-time traffic analysis, intrusion detection systems, and anomaly detection mechanisms to identify and mitigate attacks in a timely manner.
9. Engage With Law Enforcement: If the DDoS attack was severe or involved criminal activity, consider engaging with law enforcement agencies. Provide them with any available evidence and cooperate with their investigations to potentially bring the perpetrators to justice.
10. Communicate With Stakeholders: Maintain open and transparent communication with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and vendors. Inform them about the attack, the actions taken to mitigate it, and any potential impacts on services or data. Clear communication helps manage expectations and maintain trust. 11. Backup and Disaster Recovery: Review your backup and disaster recovery processes to ensure they are robust and up to date. Regularly back up critical data and test the restoration process to verify its efficacy. This will help you quickly recover in the event of future attacks. 12. Continuous Improvement: DDoS attacks are constantly evolving, so it is essential to continuously improve your security posture. Keep abreast of the latest threat intelligence, follow industry best practices, and regularly assess and enhance your security controls.
Note: Recovering from a DDoS attack requires coordinated effort and ongoing vigilance. Engage your organization's cybersecurity professionals to assist in the recovery process and to help strengthen your defenses against future DDoS attacks and report DDoS attacks to the appropriate authorities.

